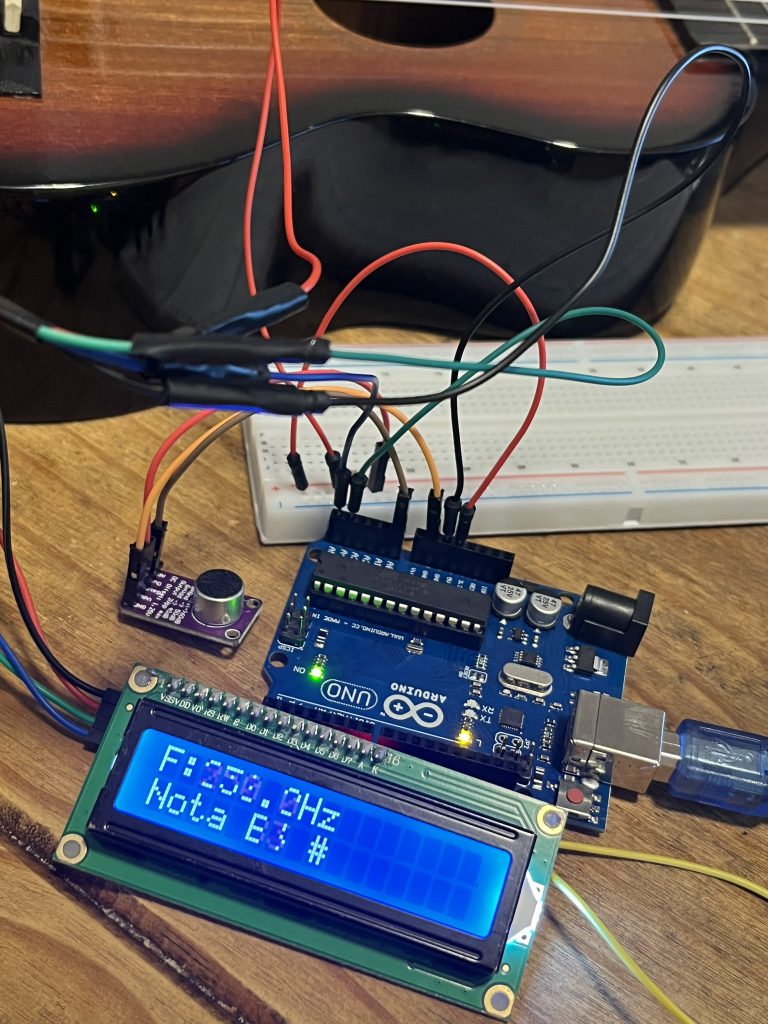
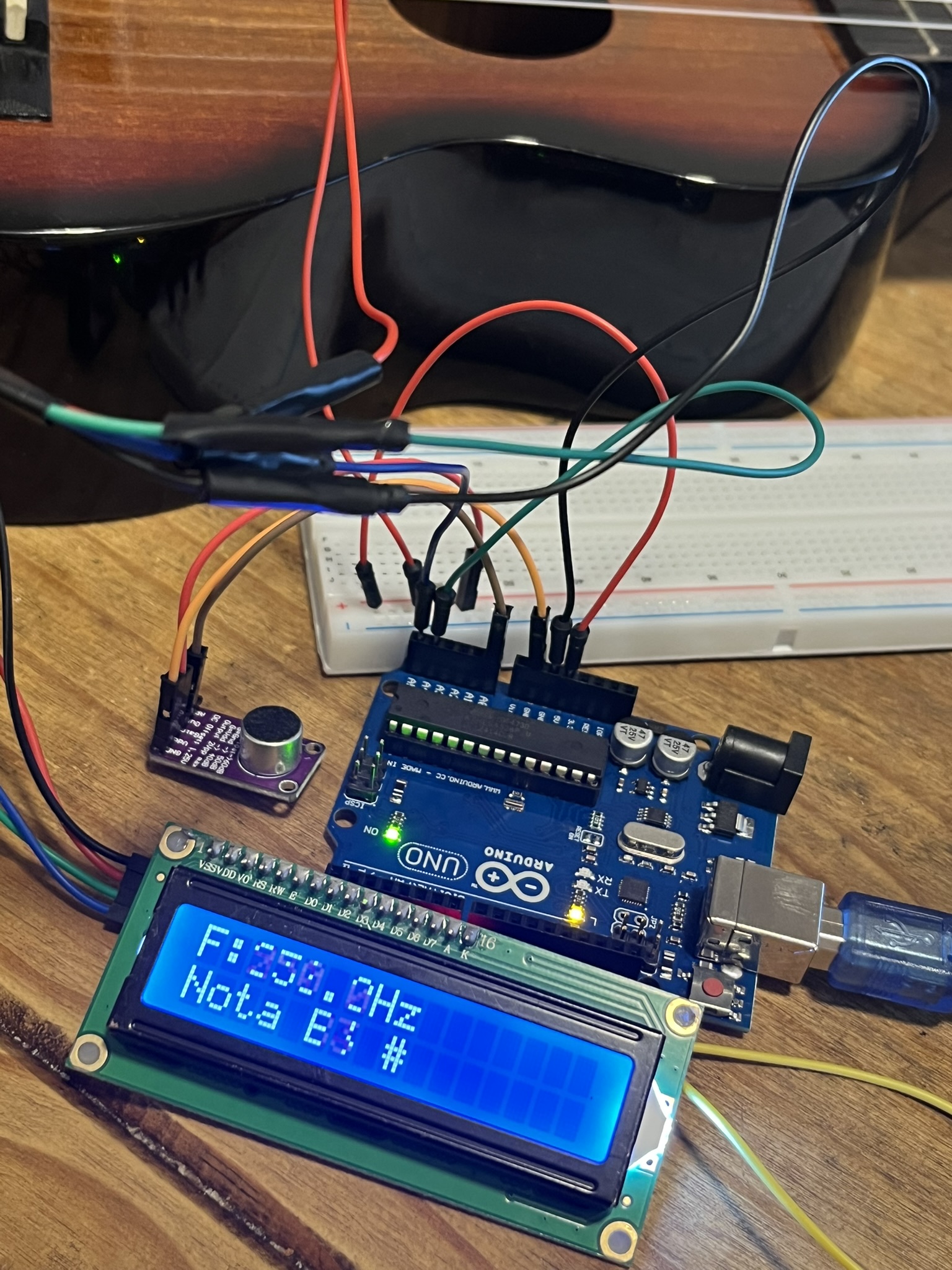
Continuando con la entrada anterior De Consola a Display, regresé a ocuparme de la conexión del display pero con arduino. El proyecto en la entrada mencionada estaba bien, pero como ocurre en ocaciones, al momento de validar, algunos problemas surgieron, el mas sencillo por llamados al include de la biblioteca del controlador del display, el LiquidCrystal_I2C.h, aquí la solución pasó por cargar desde el administrador de bibliotecas del IDE de Arduino la bliblioteca de Frank Brabander. Probé el siguiente código y… funcionó!
#include "LiquidCrystal_I2C.h"
#include <Wire.h>
LiquidCrystal_I2C lcd(0x27, 16, 2);
void setup() {
lcd.init();
lcd.backlight();
}
void loop() {
delay(1000);
lcd.setCursor(0,0);
lcd.print("Hola, Grupo!!!");
lcd.setCursor(0,1);
lcd.print("Vamo Arriba");
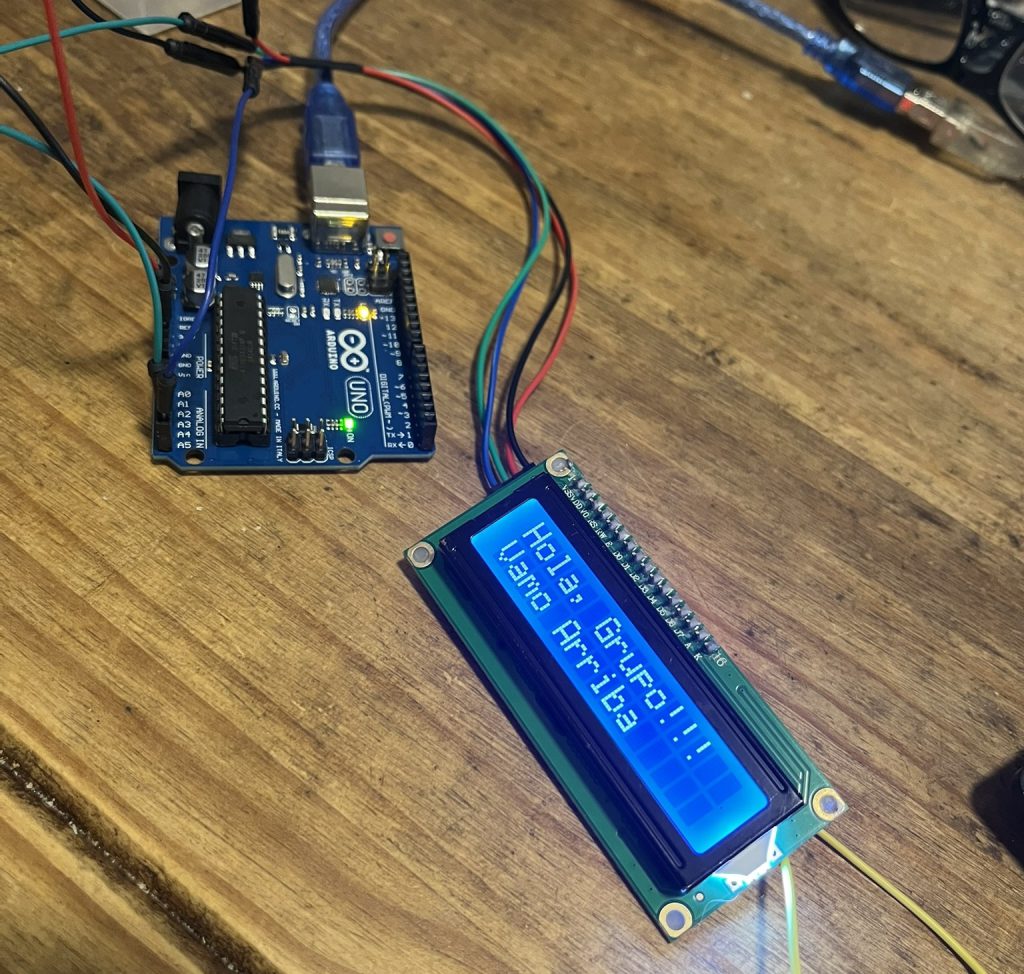
}El display desplegaba los mensajes. Sólo tuve que ajustar el brillo y habilitar la luz de fondo de la pantalla (un cable a modo de jumper).

Ahora el paso siguiente era volver con el micro. Allí el código aplicado fué el siguiente:
#include <arduinoFFT.h> // Official ArduinoFFT library v2.0.4
#define MIC_PIN A0
#define SAMPLES 128
#define SAMPLING_FREQUENCY 4000
double vReal[SAMPLES];
double vImag[SAMPLES];
ArduinoFFT<double> FFT(vReal, vImag, SAMPLES, SAMPLING_FREQUENCY);
// Standard guitar tuning (E2, A2, D3, G3, B3, E4)
struct NoteRef { const char* name; double freq; };
NoteRef notes[] = {
{"E2", 82.41}, {"A2", 110.00}, {"D3", 146.83},
{"G3", 196.00}, {"B3", 246.94}, {"E4", 329.63}
};
// Calculate cents difference
double centsDiff(double f, double ref) {
if (f <= 0 || ref <= 0) return 0;
return 1200.0 * log(f / ref) / log(2.0);
}
// Find nearest note
NoteRef nearestNote(double f) {
NoteRef best = notes[0];
double bestDiff = 1e9;
for (auto &n : notes) {
double d = fabs(centsDiff(f, n.freq));
if (d < bestDiff) { bestDiff = d; best = n; }
}
return best;
}
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Arduino Guitar Tuner (E A D G B E)");
}
void loop() {
// Capture audio samples
unsigned long microsStart = micros();
for (int i = 0; i < SAMPLES; i++) {
vReal[i] = analogRead(MIC_PIN);
vImag[i] = 0;
while (micros() - microsStart < (1000000UL * (i + 1) / SAMPLING_FREQUENCY));
}
// Remove DC offset
double mean = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < SAMPLES; i++) mean += vReal[i];
mean /= SAMPLES;
for (int i = 0; i < SAMPLES; i++) vReal[i] -= mean;
// Check for minimum amplitude to avoid noise
double maxAmplitude = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < SAMPLES; i++) {
if (fabs(vReal[i]) > maxAmplitude) maxAmplitude = fabs(vReal[i]);
}
if (maxAmplitude < 20) { // adjust threshold if needed
Serial.println("");
delay(100);
return;
}
// FFT computation
FFT.windowing(FFT_WIN_TYP_HAMMING, FFT_FORWARD);
FFT.compute(FFT_FORWARD);
FFT.complexToMagnitude();
// Find peak frequency
double maxMag = 0;
int maxIndex = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < SAMPLES / 2; i++) {
if (vReal[i] > maxMag) {
maxMag = vReal[i];
maxIndex = i;
}
}
double freq = (maxIndex * 1.0 * SAMPLING_FREQUENCY) / SAMPLES;
// Find nearest note
NoteRef n = nearestNote(freq);
double cents = centsDiff(freq, n.freq);
// Print results
Serial.print("Detected freq: ");
Serial.print(freq, 2);
Serial.print(" Hz | Nearest note: ");
Serial.print(n.name);
Serial.print(" (");
Serial.print(n.freq, 2);
Serial.print(" Hz)");
if (fabs(cents) < 5) Serial.println(" | In tune ✅");
else if (cents > 0) Serial.println(" | Sharp ↗");
else Serial.println(" | Flat ↘");
delay(200);
}Claro que esto debía funcionar junto con el display así que en un primer paso, la idea era mantener las conexiones existentes, por lo que sólo me auxilié con el protoboard para compartir el conector de 5v para el micro y el display.
El MAX9814 debe conectar de la siguiente manera:
| Módulo MAX9814 | Arduino |
|---|---|
| OUT | A0 (entrada analógica) |
| VCC | 5V |
| GND | GND |
Para el micro debe quedar:
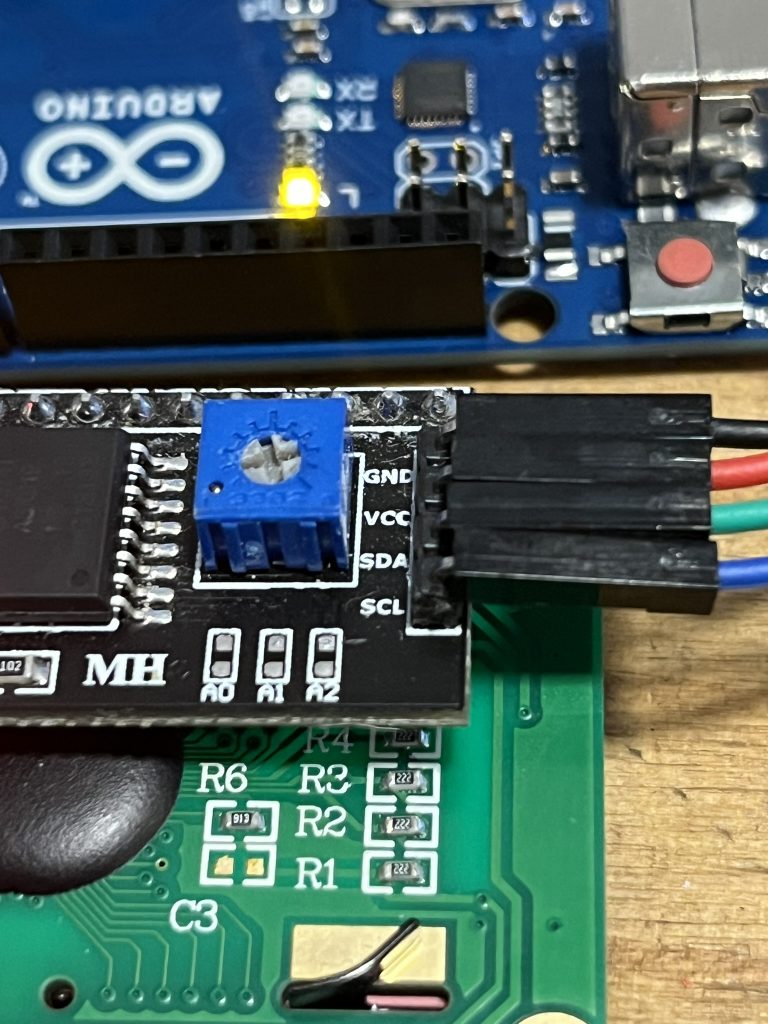
| LCD I2C | Arduino UNO Nota |
|---|---|
| VCC | 5V Alimentación |
| GND | GND Tierra común |
| SDA | A4 Datos I2C |
| SCL | A5 Reloj I2C |
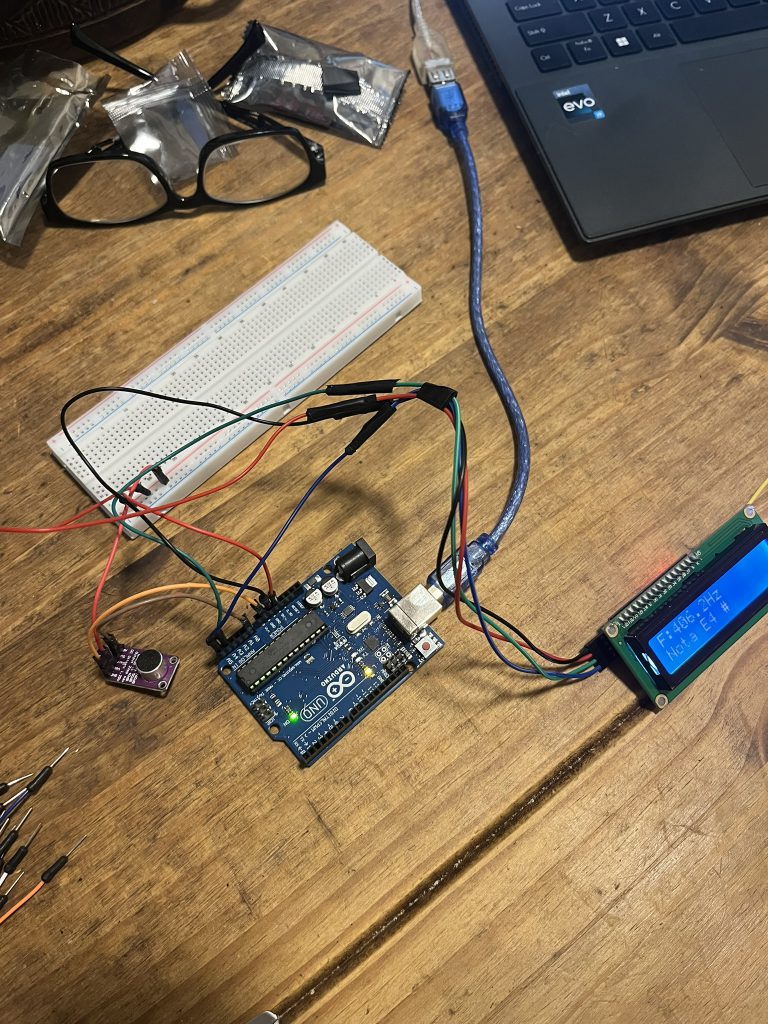
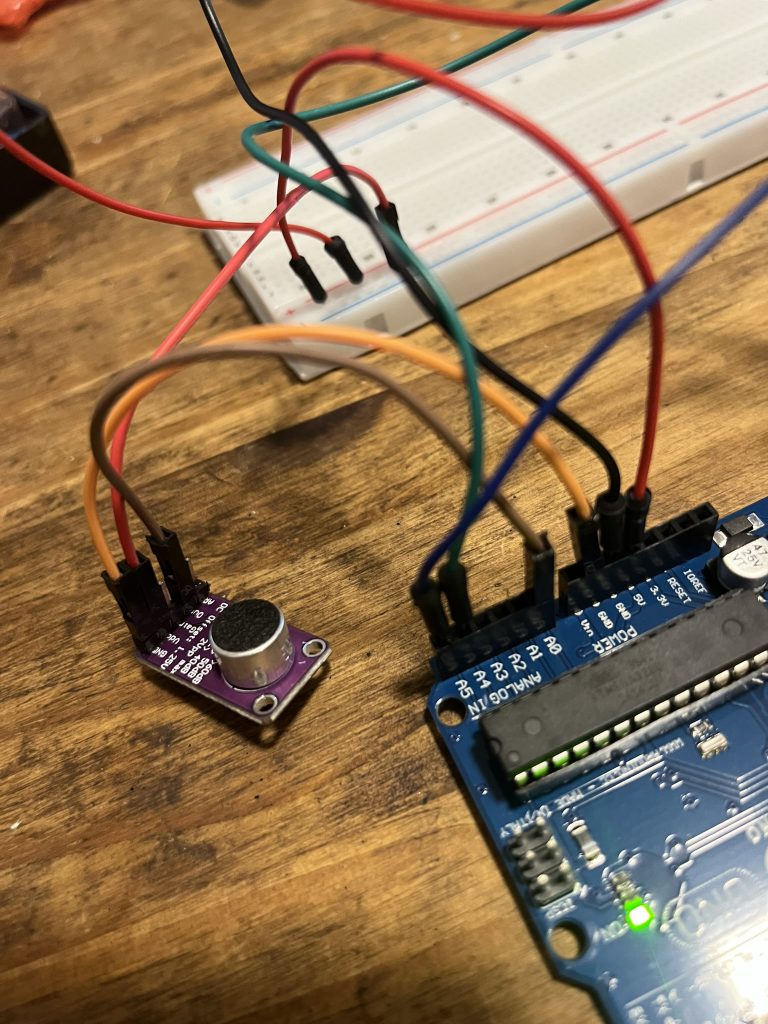
Ahora sólo restaba unir los códigos para que el resultado de la evaluación acústica se redirigiera al panel LCD. El siguiente, fué el código resultante.
#include <arduinoFFT.h> // Official ArduinoFFT library v2.0.4
#include <Wire.h>
#include <LiquidCrystal_I2C.h>
// --- LCD Config (ajusta dirección si es necesario: 0x27 o 0x3F)
LiquidCrystal_I2C lcd(0x27, 16, 2);
#define MIC_PIN A0
#define SAMPLES 128
#define SAMPLING_FREQUENCY 4000
double vReal[SAMPLES];
double vImag[SAMPLES];
ArduinoFFT<double> FFT(vReal, vImag, SAMPLES, SAMPLING_FREQUENCY);
// --- Standard guitar tuning (E2, A2, D3, G3, B3, E4)
struct NoteRef { const char* name; double freq; };
NoteRef notes[] = {
{"E2", 82.41}, {"A2", 110.00}, {"D3", 146.83},
{"G3", 196.00}, {"B3", 246.94}, {"E4", 329.63}
};
// --- Funciones auxiliares
double centsDiff(double f, double ref) {
if (f <= 0 || ref <= 0) return 0;
return 1200.0 * log(f / ref) / log(2.0);
}
NoteRef nearestNote(double f) {
NoteRef best = notes[0];
double bestDiff = 1e9;
for (auto &n : notes) {
double d = fabs(centsDiff(f, n.freq));
if (d < bestDiff) { bestDiff = d; best = n; }
}
return best;
}
// --- SETUP
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Arduino Guitar Tuner (E A D G B E)");
lcd.init();
lcd.backlight();
lcd.setCursor(0,0);
lcd.print("Guitar Tuner");
lcd.setCursor(0,1);
lcd.print("Inicializando..");
delay(2000);
lcd.clear();
}
// --- LOOP
void loop() {
// Captura de muestras
unsigned long microsStart = micros();
for (int i = 0; i < SAMPLES; i++) {
vReal[i] = analogRead(MIC_PIN);
vImag[i] = 0;
while (micros() - microsStart < (1000000UL * (i + 1) / SAMPLING_FREQUENCY));
}
// Eliminar offset DC
double mean = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < SAMPLES; i++) mean += vReal[i];
mean /= SAMPLES;
for (int i = 0; i < SAMPLES; i++) vReal[i] -= mean;
// Amplitud mínima (ruido)
double maxAmplitude = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < SAMPLES; i++) {
if (fabs(vReal[i]) > maxAmplitude) maxAmplitude = fabs(vReal[i]);
}
if (maxAmplitude < 20) {
lcd.clear();
lcd.setCursor(0,0);
lcd.print("Esperando...");
delay(100);
return;
}
// FFT
FFT.windowing(FFT_WIN_TYP_HAMMING, FFT_FORWARD);
FFT.compute(FFT_FORWARD);
FFT.complexToMagnitude();
// Pico
double maxMag = 0;
int maxIndex = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < SAMPLES / 2; i++) {
if (vReal[i] > maxMag) {
maxMag = vReal[i];
maxIndex = i;
}
}
double freq = (maxIndex * 1.0 * SAMPLING_FREQUENCY) / SAMPLES;
// Nota cercana
NoteRef n = nearestNote(freq);
double cents = centsDiff(freq, n.freq);
// --- Serial
Serial.print("Freq: ");
Serial.print(freq, 2);
Serial.print(" Hz | Note: ");
Serial.print(n.name);
if (fabs(cents) < 5) Serial.println(" | In tune ✅");
else if (cents > 0) Serial.println(" | Sharp ↗");
else Serial.println(" | Flat ↘");
// --- LCD
lcd.clear();
lcd.setCursor(0,0);
lcd.print("F:");
lcd.print(freq, 1);
lcd.print("Hz");
lcd.setCursor(0,1);
lcd.print("Nota ");
lcd.print(n.name);
if (fabs(cents) < 5) lcd.print(" OK");
else if (cents > 0) lcd.print(" #");
else lcd.print(" b");
delay(200);
}Finalmente, todo resultó.